Introduction
Big data is revolutionizing the healthcare sector and many other industries. The impact of big data transforming patient care is profound. Healthcare can now harness vast amounts of data using big data. Consequently, healthcare providers can offer patients more precise, efficient, and personalized healthcare. This article explores how big data is transforming patient care and improving healthcare outcomes. This includes examining the specific technologies and methods associated with this transformation. Big data has reshaped the landscape of modern healthcare, ranging from early diagnosis to personalized treatment plans. The future of healthcare depends upon appreciating big data’s impact.
Section 1: Early Diagnosis
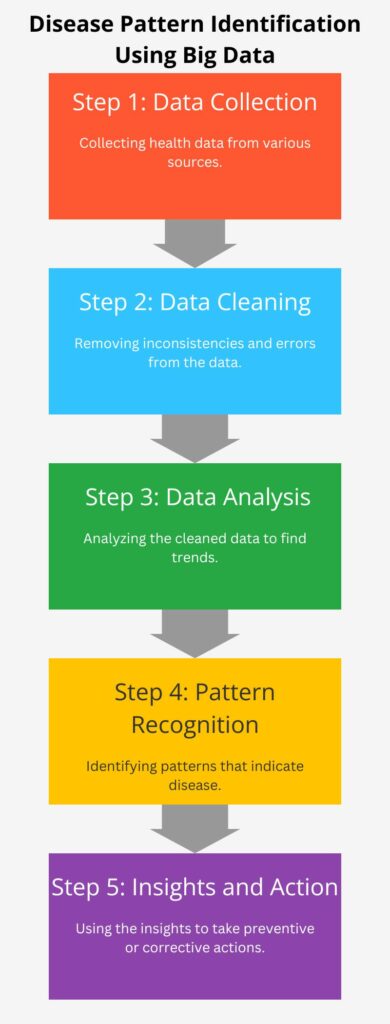
1.1 Disease Pattern Identification
Patient data often comprises large datasets with patterns indicating potential health issues. Therefore, big data applications can identify these issues by analyzing patient data sets, typically historical data. Big data algorithms can forecast potential health problems by analyzing this historical data. Prevention is better than cure, which is a crucial benefit of forecasting. This provides an earlier diagnosis of health issues and early intervention. Using predictive analytics makes it easier to identify potential health problems at an earlier stage. This enables medical professionals to treat possible health issues early and proactively prevent significant problems.
1.2 Reducing Diagnostic Errors
Limited data hampers diagnosis, making it an inexact science in which more available data improves accuracy. However, data analytics can cross-reference symptoms with vast medical databases, improving diagnosis accuracy. Therefore, this reduces the likelihood of an incorrect diagnosis leading to severe consequences. One example is when big data distinguishes between different types of pneumonia based on chest X-rays alongside other patient data. This also helps to reduce unnecessary and redundant treatment and their associated costs, making healthcare less expensive. This makes diagnosis more data-driven and less speculative, leading to better health outcomes. This also improves trust and satisfaction for both patients and their family members.
1.3 Enhancing Screening Programs
Big data can identify trends and patterns by analyzing vast amounts of health data. Therefore, big data can contribute to optimizing population health screening programs, resulting in several benefits. It can also improve targeted interventions by identifying high-risk groups based on various factors. Big data also facilitates early screening, which increases the chances of successful treatment outcomes. Also, when these screening programs target high-risk populations, they will reduce unnecessary screening, making programs more cost-effective.
Consequently, the efficient allocation of healthcare resources will ensure they are available where they are most needed. Big data can also develop personalized screening programs based on individual risk factors. And continually monitor screening program performance to identify areas for improvement.
1.4 Real-Time Monitoring
Wearable devices that collect real-time health data from patients can potentially generate vast amounts of data. Big data can store and analyze this data to detect early signs of health deterioration. This provides continuous monitoring to assist in timely medical intervention. Because this data is in real-time, it enables personalized healthcare. Subsequently, this improves the overall quality of patient care. Big data also provides real-time monitoring that enables more effective management of chronic conditions. Real-time data analysis also benefits early detection, which can reduce hospital readmission rates. Another benefit is that these devices provide continuous health data that can enhance the accuracy of diagnoses.
1.5 Improving Public Health Surveillance
Big data’s ability to derive trends from datasets allows it to enhance surveillance of public health trends. Analyzing large datasets in real-time can also help track the spread of infectious diseases. Data analytics can also help predict and manage outbreaks. This results in making public health responses more effective and timely. Expanding this on a global scale can support global health initiatives. In turn, this identifies emerging health threats more quickly. Because big data performs data integration data from multiple sources, it also improves accuracy. An additional benefit is that it aids resource allocation during health crises.
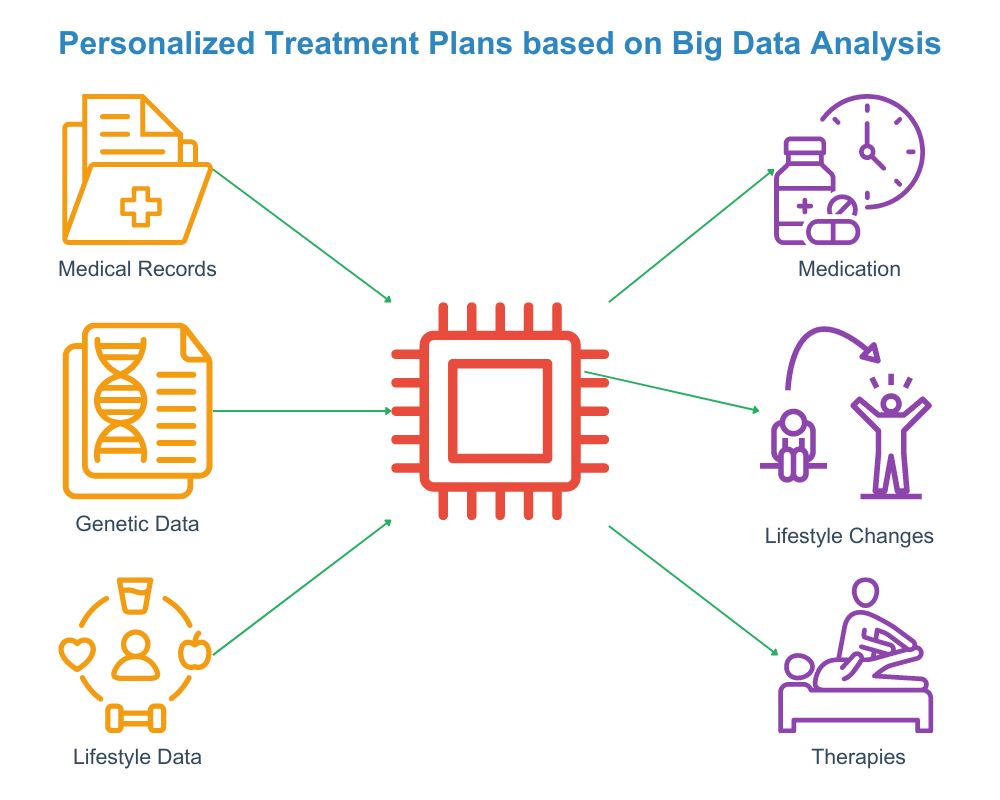
Section 2: Personalized Treatment Plans
2.1 Tailoring Treatments to Individual Patients
Big data allows the customization of treatments by applying data analytics to patient data. This is possible because big data analyzes a patient’s genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors in an integrated manner. Therefore, medical professionals can use these insights to provide personalized treatment plans for better patient outcomes. An added benefit is that they minimize the adverse reactions to treatments. Customized treatment plans also enhance patient adherence to treatment regions; dynamic adjustments to those plans are now possible. These interventions are now far more data-driven, improving their effectiveness. A final benefit is that personalized treatments foster patient satisfaction and trust due to big data transforming patient care.
2.2 Optimizing Medication Management
Data analytics makes prescriptions for medication dosages far more data-driven. This lessens the need to adjust dosages based on trial and error, enhancing precision in medication use. It can also utilize patient-specific factors for optimal results and reduce the risk of side effects. Overall, it contributes significantly to medication management and improves treatment efficacy. Consequently, this helps to ensure patient safety and well-being. Big data also provides ongoing monitoring of treatments, allowing ongoing adjustment and improvement. Finally, big data can provide insight into patterns of drug interactions.
2.3 Enhancing Chronic Disease Management
Big data also supports chronic disease management, such as diabetes and hypertension. Big data enables continual monitoring of patient progress and allows health professionals to adjust treatments accordingly. Data-driven insights also improve long-term health outcomes, making chronic disease management more efficient. An added benefit is that predictive analytics can identify potential complications early. These benefits combined enhance patient engagement and self-management. Therefore, patients can experience a better quality of life. Finally, given that patients often have several providers, these providers can better share data that improves coordinated care. This demonstrates how big data is transforming patient care.
2.4 Facilitating Precision Medicine
Precision medicine is when medicine is far more data-driven. Big data makes precision medicine possible, which reduces trial and error in prescribing medication. Therefore, precision medicine offers more highly effective treatments, delivering the most suitable therapies to patients. An example is when precision medicine uses genetic information to tailor treatments. Big data also processes the latest real-world data. Therefore, it continually refines treatment protocols and supports continuous research and development. Finally, big data reduces overall healthcare costs by reducing trial and error.
2.5 Integrating Multidisciplinary Care
Patients often have multiple healthcare providers, making collaboration essential. Because big data provides analysis and management of integrated data, care coordination is more data-driven and, thereby, more effective. Consequently, this fosters collaboration among healthcare providers and integrates their various specialties. This benefit makes patient care far more comprehensive and addresses all aspects of patient health. Another benefit is that it streamlines communications between providers. Integrated data also allows providers to develop holistic collective care plans for their patients. Providers, therefore, can enhance patient experiences through their collective efforts.
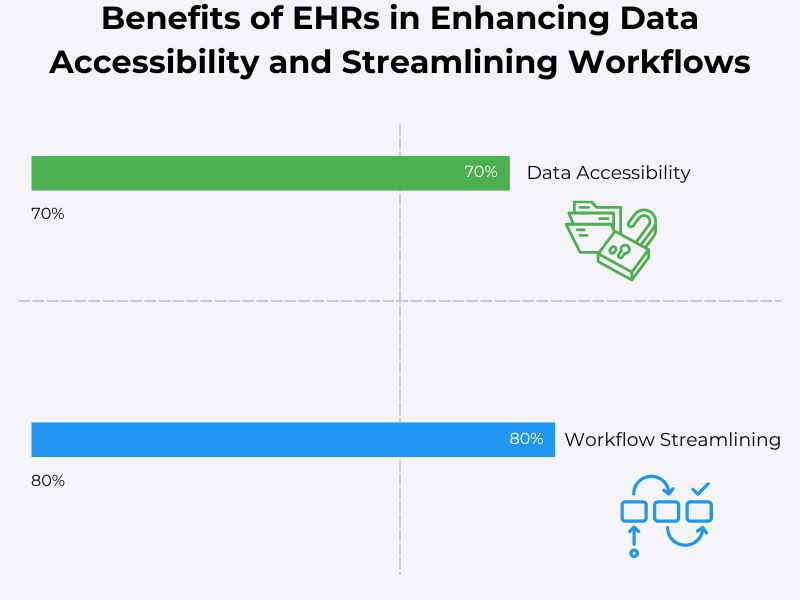
Section 3: Electronic Health Records (EHRs)
3.1 Enhancing Data Accessibility
Big data enables the management and use of EHRs containing complete patient data collected from various sources. Additionally, updating EHRs with the latest patient data in real time is possible. EHRs ensure that healthcare providers have complete patient information and can improve continuity of care. They also reduce duplication of tests and procedures and enhance patient safety and care quality. Healthcare providers can make critical decisions because they can access timely patient data. EHRs also facilitate seamless transitions between care settings and also support patient involvement in their care. This shows how big data is transforming patient care.
3.2 Streamlining Clinical Workflows
Healthcare has been highly fragmented, and EHRs constitute a significant step in addressing this. An immediate benefit is that they reduce the paperwork needed to deliver healthcare services. Furthermore, they streamline administrative and clinical workflows, improving healthcare efficiency and cost savings. Along with facilitating the automation of routine tasks, EHRs enable healthcare providers to focus more on patient care. EHRs also support better resource management and contribute to making clinical documentation more accurate.
3.3 Facilitating Data Sharing
Patients commonly interact with multiple healthcare systems that have poorly shared patient data in the past. EHRs address this issue by enabling secure sharing of patient data across different healthcare systems. Effective data sharing improves coordination between different healthcare providers, enhancing the overall quality of care. Furthermore, healthcare providers have timely access to critical patient information. EHRs support integrated healthcare delivery and strengthen collaborative care models. Beyond patient care, EHRs facilitate multi-site research and studies, and policymakers can enhance public health strategies using patient data.
3.4 Supporting Decision-Making
A critical benefit of big data is that it facilitates informed and data-driven decision-making. Therefore, EHRs provide valuable data for data-driven clinical decision-making and offer evidence-based recommendations. Also, decision support tools can utilize EHRs to improve diagnostic accuracy. This allows healthcare providers to enhance treatment planning and contribute to better patient outcomes. Additionally, EHRs provide easy access to clinical guidelines and support personalized care plans. Health providers and researchers can better refine treatment protocols using data analytics from EHR data. This exemplifies how big data is transforming patient care.
3.5 Ensuring Data Security and Privacy
Moving from fragmented patient record-keeping to EHRs facilitates far better patient data management. This better protects patient data by allowing the implementation of robust security measures. These include placing encryption and access controls that prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information. Furthermore, EHRs will enable the implementation of advanced security protocols that minimize data breaches. Healthcare management can also apply regular security audits to EHR systems. Overall, this contributes to ensuring patient confidentiality and building patient trust. Another critical benefit is that EHRs strengthen compliance with regulatory standards.
Section 4: Wearable Technology
4.1 Monitoring Vital Signs
Big data technology makes it possible to utilize data from wearable devices continuously and on time. Wearable devices track vital signs like heart rate and blood pressure. Combined with big data, they provide continuous monitoring with real-time health insights. This also assists with detecting early signs of health issues while supporting proactive healthcare. Additionally, patients can manage their healthcare better, and the associated data informs healthcare decisions. Along with health issues, wearable devices also detect anomalies early, reducing the likelihood of complications. When integrated with EHRs, they provide comprehensive monitoring of patient’s health.
4.2 Promoting Physical Activity
Patients need to participate actively in their overall healthcare, including physical activity. Wearables encourage physical activity through fitness tracking and provide feedback on exercise routines. Big data assists with designing personalized fitness plans from wearable device data. Wearable devices constantly remind patients of their overall health and motivate them to stay active. Healthcare providers working with their patients can use activity data to set and achieve health goals. Wearable devices allow patients to track and celebrate fitness progress, enhancing their motivation. Furthermore, these devices’ community features facilitate social support and strengthen patients’ motivation. All these benefits combine to improve overall health.
4.3 Managing Chronic Conditions
Wearable devices assist in managing chronic conditions through monitoring symptoms and treatment adherence. Furthermore, their data assists in adjusting treatment plans, making chronic disease management more effective. Wearable also makes the data available to the patient, improving patient engagement in the care of healthcare providers. Wearables generate real-time data for timely intervention, and healthcare providers can dynamically adjust treatment plans using wearable data. Wearable devices make data sharing possible, which enhances healthcare provider communication.
4.4 Enhancing Patient-Doctor Communication
Since wearables produce continuous and timely data, they enable continuous communication between patients and healthcare providers. Healthcare providers can also use this data for remote monitoring and perform timely medical intervention when needed. Additionally, healthcare providers can promptly address patient concerns. Wearable data is also used for remote consultations. Therefore, they support telemedicine and virtual care. This improved communication enhances patient care and satisfaction, showcasing how big data is transforming patient care.
4.5 Supporting Mental Health
Wearable technology has the potential to transform mental health by monitoring stress and mental health indicators. The following mental health factors that wearable can monitor include sleep patterns and activity levels. Big data can use wearable data to provide insights into mental well-being and support mental health treatments. Upon application of treatments, wearables then track progress in these interventions. Also, real-time feedback assists providers in managing mental health proactively. Finally, providers can take a holistic approach to delivering health services to patients.

Section 5: Telemedicine
5.1 Expanding Healthcare Access
Big data is necessary to promote the growth of telemedicine. Telemedicine expands the reach of healthcare services, including providing access to remote and underserved areas. This allows health providers to offer specialized care regardless of location and benefits rural regions significantly. Telemedicine will enable patients to receive care from the comfort of their homes. Also, this will reduce the need to travel to healthcare facilities. Overall, telemedicine reduces barriers to healthcare access.
5.2 Facilitating Remote Consultations
Telemedicine will enable patients to have remote consultations with healthcare providers, offering them convenience and flexibility. This will also save time and reduce healthcare costs while providing patients timely medical advice and continuous care. A further benefit is reduced wait times. Telemedicine allows providers to manage follow-up appointments remotely, making them more manageable. Telemedicine also improves access to specialist care.
5.3 Enhancing Chronic Disease Management
Big data allows telemedicine to support remote monitoring of chronic conditions, primarily through wearables. This, in turn, enables remote check-ins with healthcare providers and improves disease management while reducing hospital visits. A further benefit is that big data through telemedicine provides continuous monitoring that allows for timely adjustments to treatment. This also makes chronic disease management more personalized and effective. Along with regular virtual check-ins, it enhances patient engagement, and patients experience better health outcomes.
5.4 Improving Emergency Response
A major healthcare challenge is delivering healthcare services in an emergency. This is due to the distance between the patient and the healthcare facility. Telemedicine technologies can significantly address this by allowing remote consultations to guide emergency interventions. Telemedicine allows real-time consultations to support emergency responses and provide immediate medical advice during emergencies. These real-time expert consultations can guide emergency medical teams and first responders during an emergency. This will also facilitate quick decision-making in these critical situations. A further benefit is that real-time data sharing will enhance emergency response capabilities. Ultimately, this timely medical care will save lives.
5.5 Supporting Mental Health Services
Big data through telemedicine can expand access to mental health services, primarily through offering virtual counseling and therapy sessions. These virtual sessions offer flexibility and privacy for patients. Patients can receive mental health support at home while reducing the stigma associated with seeking mental health care. Telemedicine also allows providers to provide continuous mental health support. Additionally, it makes these services more accessible and affordable. This contributes to enhancing the overall well-being of patients.
Conclusion
This article shows that big data’s impact on health care is profound and far-reaching. It shows how big data revolutionizes patient care through predictive analytics, personalized treatment plans, EHRs, wearable technology, and telemedicine. These advancements have led to earlier diagnosis, tailored treatments, and improved patient outcomes. Big data’s future potential will significantly include its role in healthcare. Big data will continue to transform patient care as the technology develops.


