Welcome to the beginner’s Big Data guide, your essential resource for understanding, collecting, and analyzing big data effectively.
Beginner’s Big Data Guide To Big Data Basics
Introduction to Big Data
Technological advances in digital computing have given rise to the need to process very large datasets and derive insight from those datasets. The field of big data for beginners encompasses the tools and technology needed to process and analyze these datasets to derive meaningful information that includes patterns, trends, and insights. Processing these datasets not only has to address their size but the rate at which this data is generated, and there often, the data is not consistently organized but has a variety of data structures, including the data being unstructured. Information derived from these datasets makes decision-making and strategic planning far more data-driven. Innovation also benefits from being based more on data than hypotheses.
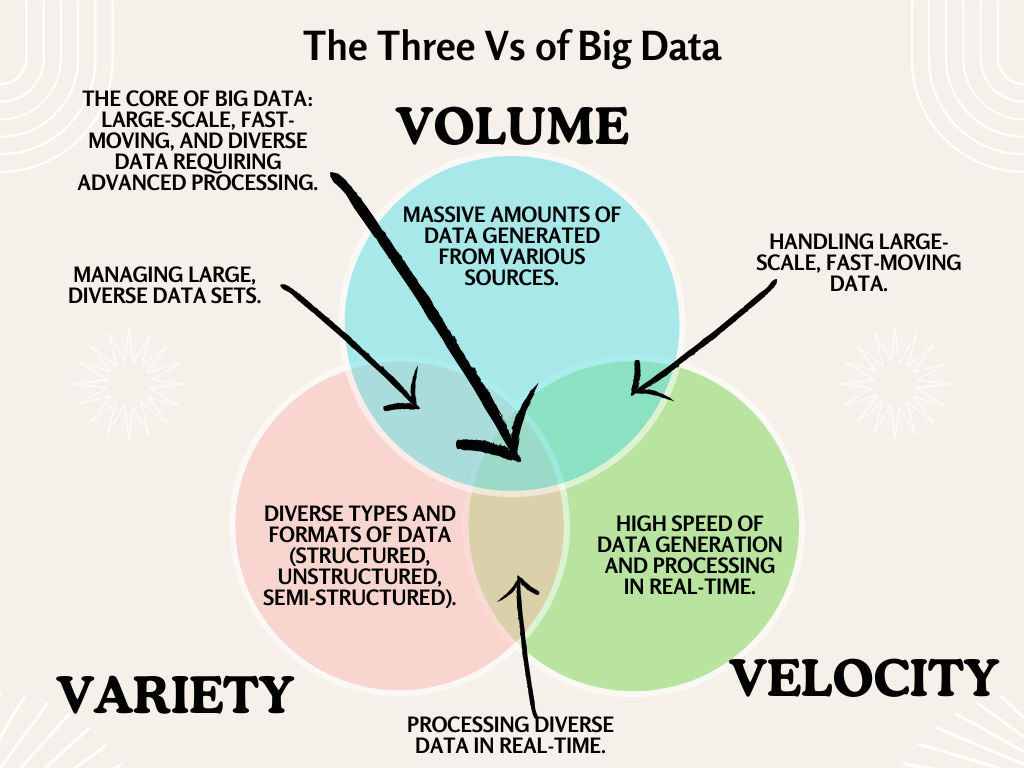
The Three Vs of Big Data
Dataset characteristics mentioned above in terms of their size, rate of generation, and varied structures are represented by the three Vs. The first V is volume, representing the size of generated datasets and the storage demands to manage these datasets. The second V is velocity, representing the rate at which datasets are generated and the processing demands for their timely processing. The third V is variety, representing the wide range of data formats that need to be handled, ranging from simple text to images and videos. This foundational concept is crucial in the Beginner’s Big Data Guide.
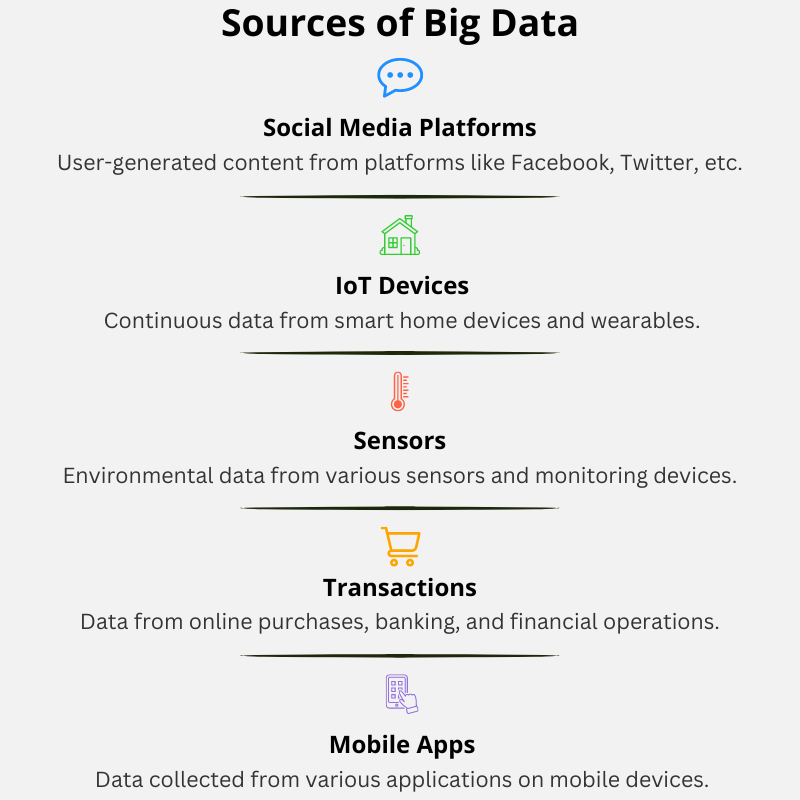
Sources of Big Data
The field of big data exists because technological advances have resulted in the creation of many sources that generate such datasets with high volume, generated at high velocity, and highly varied data formats. These sources include and are not limited to social media platforms generating user-generated content, sensors, IoT devices continuously collecting data from their physical environments, transactions including online purchases and financial operations, and mobile devices from all their apps.
Challenges of Big Data
Big data’s explosive growth results in necessary safeguards scrambling to address all the harmful consequences of big data. The first challenge is ensuring data is accurate, consistent, and complete, guaranteeing data quality. The second challenge is protecting data from unauthorized access and breaches, which is termed cybersecurity. The third challenge is properly and appropriately handling personally sensitive information, which is termed data privacy. There are many other challenges, but most fall under these umbrella terms.
Big Data in Organizations
There is a growing number of public and private organizations where big data has become part of the very fabric of their operations. These include and are not limited to retailers, healthcare providers, financial institutions, transportation companies, and smart cities.
Beginner’s Big Data Guide On Collecting Data Effectively
Formulating Data Collection Goals
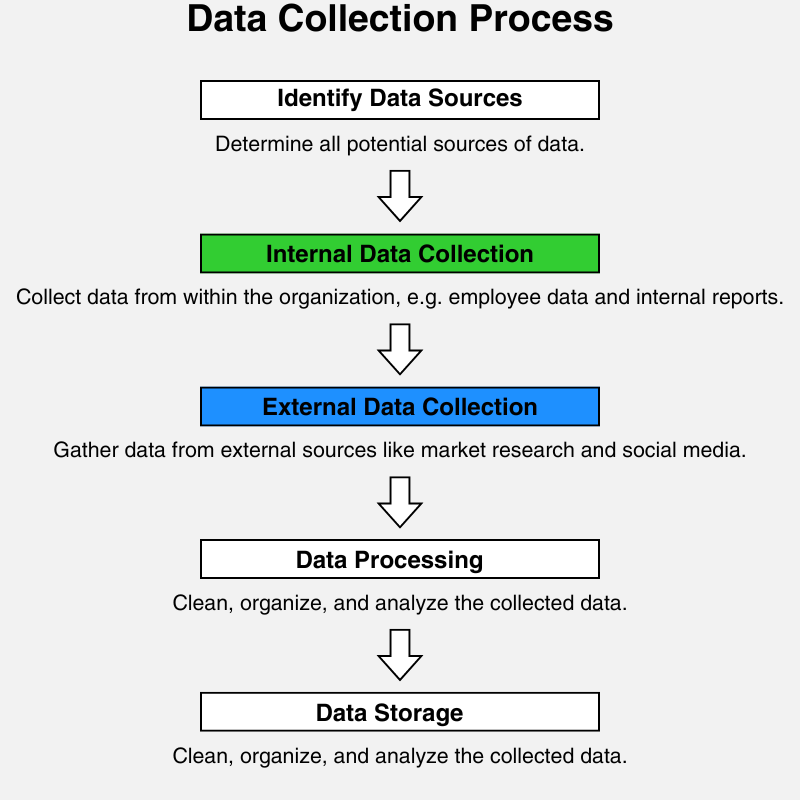
Big data is a relatively young field that necessitated the development of new paradigms to handle size and complexity. However, successful big data implementation comprises many of the principles rooted in conducting successful research projects. Like the Hitchhikers’ Guide to the Galaxy, formulating the question to be answered is the essential first step prior to any endeavor of successfully implementing any project, including Big Data. This begins with the organization understanding its objectives and then understanding the data needed to obtain its objectives. These are broken further into strategic goals, and decision-making needs where it is necessary to identify data to solve specific problems or improve operations. It is also important that goals are regularly reviewed in terms of their alignment with the organization’s changing needs. Understanding the differences between these data sources is crucial for anyone following a beginner’s big data guide.
Identifying Data Sources
Next, it is important to identify internal and external data sources relevant to the organization’s goals and assess their reliability. Data sources also encompass primary and secondary data. Primary data includes but is not limited to sales records, customer interactions, website analytics, mobile app data, and IoT devices. In contrast, secondary data includes but is not limited to industry reports and media insights.
Data Collection Methods
Closely aligned with data source selection are data collection methods. This is relatively straightforward for data from internal IT systems since many fine tools are available, and Internal data includes detailed activity data stored in transaction logs. Data from an organization’s physical environment is obtainable through sensor technology and IoT devices. There are several means of collecting external data, from conducting customer surveys to using APIs to access and collect data from external sources. Collected data needs to be stored, and various big technologies are designed, including but not limited to data warehousing and NoSQL databases.
Ensuring Data Quality and Compliance
Two important considerations in collecting data are guaranteeing data quality and ensuring compliance with the growing regulations around data management. Big data provides technical solutions around data cleaning that remove inaccuracies, duplicates, and inconsistencies. These need to be complemented by organizational processes and policies, and ongoing auditing by both automated tools and manual processes is necessary. In addition to data quality, regulatory frameworks cover data privacy and transparency, and organizations must ensure they comply with these requirements.
Automating Data Collection
Organizations should seek to automate and streamline their data collection, given that the amount of data and the rate of data generation will continually increase. Big data provides an array of tools and technologies that can be employed. Finally, organizations must monitor the data collection process and establish regular audits assessing its effectiveness. In addition to regular audits, day-to-day monitoring of data collection activities is needed, including the ability to generate alerts whenever anomalies or disruptions occur in the workflows.
Processing and Managing Data
Data Preprocessing
Once data is collected it is necessary for preprocessing to be performed prior to any analysis for insights and understanding that can be obtained from it. Data management is needed to maintain data integrity and is one of the steps that ensure organizations comply with regulatory frameworks imposed by many powerful jurisdictions.
Data Preprocessing Activities
There are several activities that comprise data preprocessing, including data cleaning, data formatting, and data integration. Whereas some data preprocessing elements may appear in the data collection stage, data preprocessing is regarded as a separate stage following data collection. Data cleaning involves removing errors and inconsistencies that potentially render data harmful when wrong insights are derived, resulting in bad or harmful decisions. Analyzing data often requires data to be in a certain format that is different from data collected from its sources; therefore, data format needs to be transformed into a format compatible with data analysis. Data most likely comes from various sources and needs to be integrated to produce a comprehensive dataset for analysis.
Data Management Activities
Management of data is responsible for the entire data lifecycle and comprises data storage, data processing, data security, data quality assurance, and data disposal or deletion. Data storage and data processing allow analytic tools to perform algorithms that derive data insights used for data-driven decisions. Understanding these aspects is crucial for anyone following a beginner’s big data guide. Different tools supporting these activities are compatible with specific data and requirements. Examples of well-known and commonly used tools include Apache Hadoop, Apache Spark, and NoSQL databases. Apache Hadoop provides distributed storage, and its processing can handle large datasets. Apache Spark provides in-memory data processing that results in high-speed data analytics. NoSQL databases enable the efficient storage of large volumes of unstructured data.
(For a deeper dive into Apache Spark and its role in big data analytics, check out our Apache Spark Big Data Analytics Guide.) To further explore how Apache Spark is architected and optimized for large-scale data processing, see our Apache Spark Architecture: Big Data Guide.
Data Security
Data security is an essential data management activity both from a data safety standpoint and from a regulatory requirements standpoint. Sensitive and confidential information must be protected from unauthorized access and potential tampering, resulting in potentially very harmful consequences. While organizations need to deploy an entire arsenal of data security measures, it is essential that data is encrypted for both storage and transmission. Besides automated security tools, organizational policies, practices, and training are needed to complement automated data security.
Maintaining Data Quality
While data preprocessing is essential, it is also important and necessary that data quality is maintained throughout the entire data lifecycle. Like data security, this comprises both automated tools and personnel involvement. Automated data quality tools continually monitor data for error identification and correction. Personnel involvement involves policies, procedures, practices, and training to guarantee data quality.
Data Deletion
Finally, data deletion is an important activity due to data management costs and regulatory requirements around personal and sensitive data.
Analyzing Data for Insights
Defining Analysis Goals
The main purpose of data collection, processing, and management is the ability to perform data analysis and then use its results to subsequently perform key activities, including but not limited to decision-making, communication, and prediction. Similar to data collection, data analysis goals need to be clearly defined and aligned with the organization’s objectives to be effective, sharing many principles rooted in conducting successful research projects. Furthermore, these objectives must be reviewed and refined regularly due to a changing business environment.
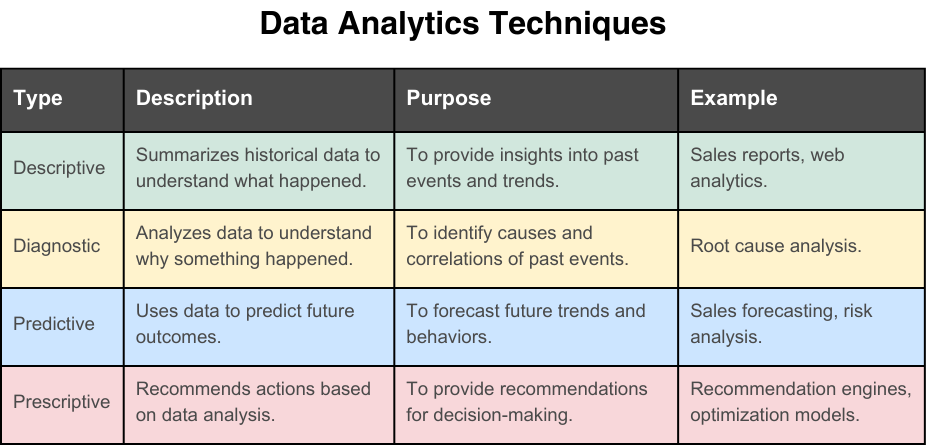
Types of Data Analytics
There are various analysis techniques whose selection and combination depend on the organization’s goals and objectives. Descriptive analytics present summaries of historical data and allow an organization to understand past performance. Whenever an organization wants to better understand the causes of past outcomes and issues, diagnostic analytics are employed. Strategic decisions depend upon forecasts of future trends, and predictive analytics on historical data can provide more reliable and data-based forecasts. Operational activities rely on optimal decision-making and actions can be recommended by prescriptive analytics. Given the complexity of many scenarios, it is necessary to combine these techniques to provide comprehensive insights.
Data Analytics Tools
There are many data analytics tools available, and organizations commencing their big data journey should look to more general tools and proceed to more specific tools as they become more sophisticated in handling big data. An important component of these tools is data visualization, allowing users to understand what the data represents intuitively. Several tools are accessible by beginners and support a wide range of analytical needs, making them ideal for a beginner’s big data guide, including Microsoft Power PI, Tableau Public, and Google Analytics; however, the last is specific to website behavior.
Interpreting and Utilizing Insights
Meaningful insights can only be derived from sound interpretation of data analytics outcomes, where these findings are translated into actionable strategies to achieve organizational objectives. Key components are visualization and presentation of outcomes to demonstrate how insights were obtained and communicate with stakeholders for better-informed decision-making. It is also important to continually validate analytics outcomes with further data collection and analysis to build confidence in understanding.
In many scenarios, big data processing enables or supports the ability to experiment and perform A/B testing that can significantly build confidence in strategic decisions.
Collaboration and Continuous Improvement
Insight from data analytics involves both technical tools and organizational processes. Team collaboration and stakeholder involvement are essential in making sound interpretations and decisions from data analysis. Collaborative tools are essential for information sharing and allowing teams to arrive at collective interpretations and perform collective decision-making that will enhance the quality and applicability of data-driven decisions.
In addition to continuously reviewing organization objectives, it is important to measure analysis effectiveness. Organizations should also apply feedback to analysis techniques to implement continuous improvement.
Resources and Further Learning
Although big data is relatively young, it has experienced explosive growth. It encompasses a wide and deep body of knowledge. This blog article can only provide a very high-level overview. Therefore, if the reader wants to continue their big data journey, they must read more extensively. They should also attend courses and seminars for deeper understanding.

Recommended Books
Several books are more detailed than this article but still directed at beginners. Highly recommended books for beginners include “Big Data: A Revolution That Will Transform How We Live, Work, and Think”. Another book that keeps concepts simple and easy to understand is “Big Data for Dummies.”. “Data Science for Business” demonstrates how data science fits into an organization. It also demonstrates how Big Data can be used for competitive advantage.
Online Courses
Online courses are revolutionizing education, and there are many online courses available on big data. These range from introductory courses to in depth and focusing on different subject areas of big data. LinkedIn offers accessible courses around big data technology and applications. Udemy provides many tutorials on specific big data tools, including Hadoop and Spark. Many top universities offer comprehensive courses on big data fundamentals through the Coursea platform. Other institutions like Harvard and MIT provide big data courses through edX. Finally, DataCamp is a specialist online learning platform that provides interactive learning around data manipulation and analysis.
Webinars and Workshops
Alongside online learning are webinars and workshops provided by big data communities. These include Data Science Central and Big Data Learning. Companies like Microsoft and IBM along with management consulting firms like Accenture and Deloitte also offer these and training services. These are worth consideration whenever an organization needs to develop big data training for its members.
Case Studies
There are numerous organizations deriving a distinct competitive advantage through embedding big data into their operations. Netflix pioneered using big data to personalize content recommendations. Amazon innovated the use of big data in optimizing its supply chain management. Likewise, Walmat improved customer experience and operations through its big data strategies. There are also many healthcare providers that have used big data to enhance patient care and treatment outcomes. Also, IBM publishes case studies explaining the application of big data in various industries.
Staying Current
Finally, it is important to stay current, and there are various forums that enable this. The forums include online communities that allow members to remain updated. Several examples include LinkedIn groups and Reddit. Several data science-specific groups exist, including Data Science Central and the Kaggle community. Blogs and websites that provide new developments and innovation updates include Datafloq, TechCrunch, and Wired. Attending conferences like Strata Data Conference is also an opportunity to remain current and network.


